Treatment of Gingivitis
Treatment of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common condition that affects the gums that surround the teeth. It is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the gums, which can lead to discomfort, bleeding and bad breath. Understanding the causes, symptoms and treatment of gingivitis is vital to maintaining good oral health.
What causes gingivitis?
Gingivitis is mainly caused by poor oral hygiene. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on the teeth and along the gum line, it can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. Other factors that can contribute to the development of gingivitis are hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, certain medications, smoking, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes. It is important to note that poor oral hygiene is the main culprit for gingivitis, so maintaining a good oral hygiene routine is essential to preventing and treating this condition.
Common symptoms of gingivitis
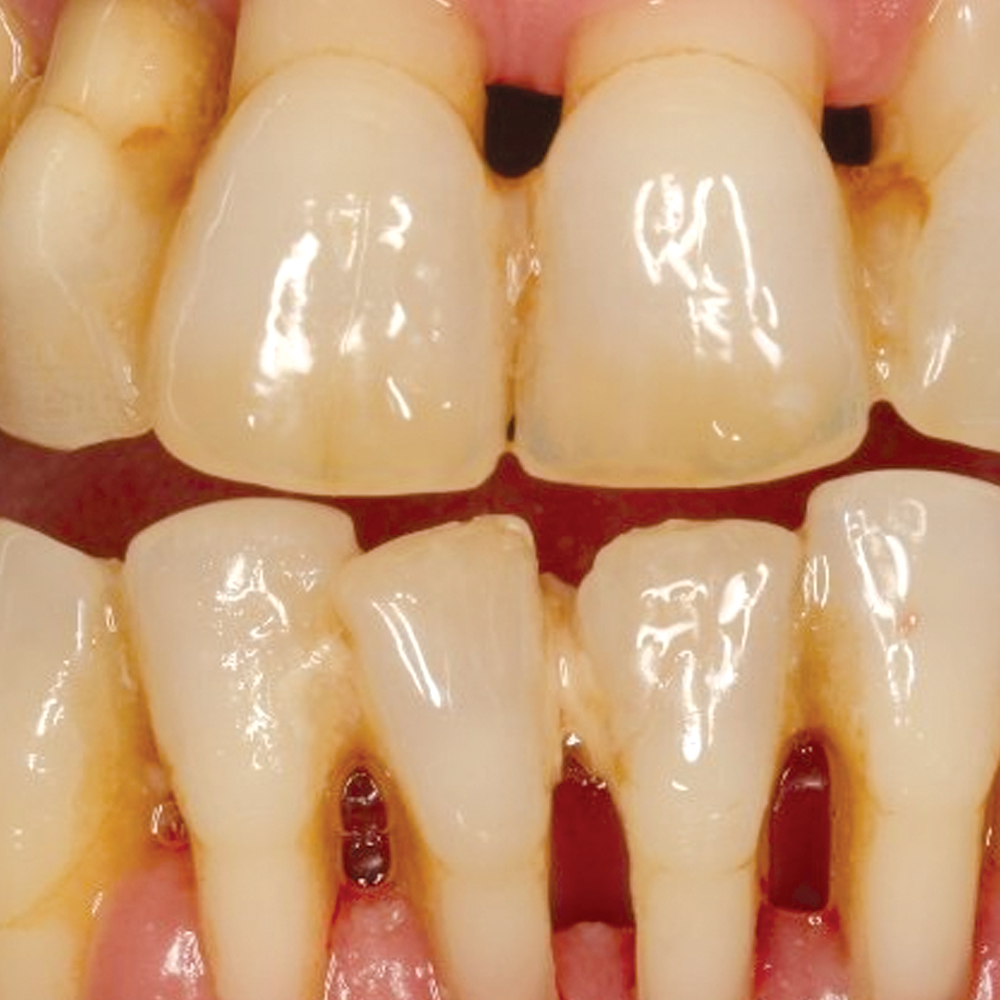
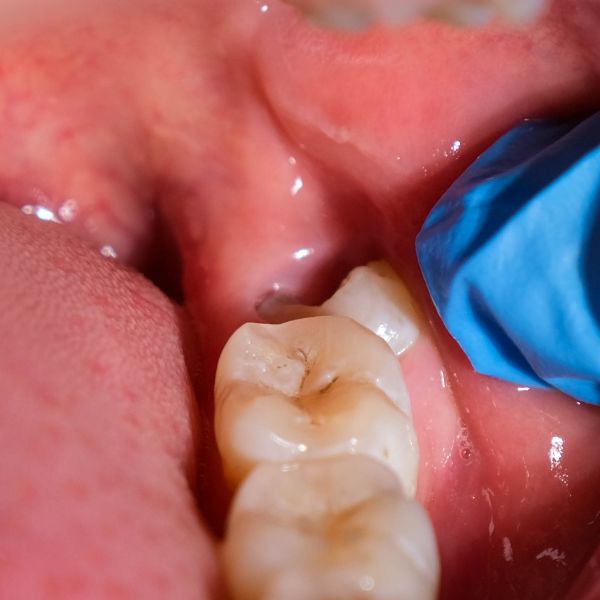
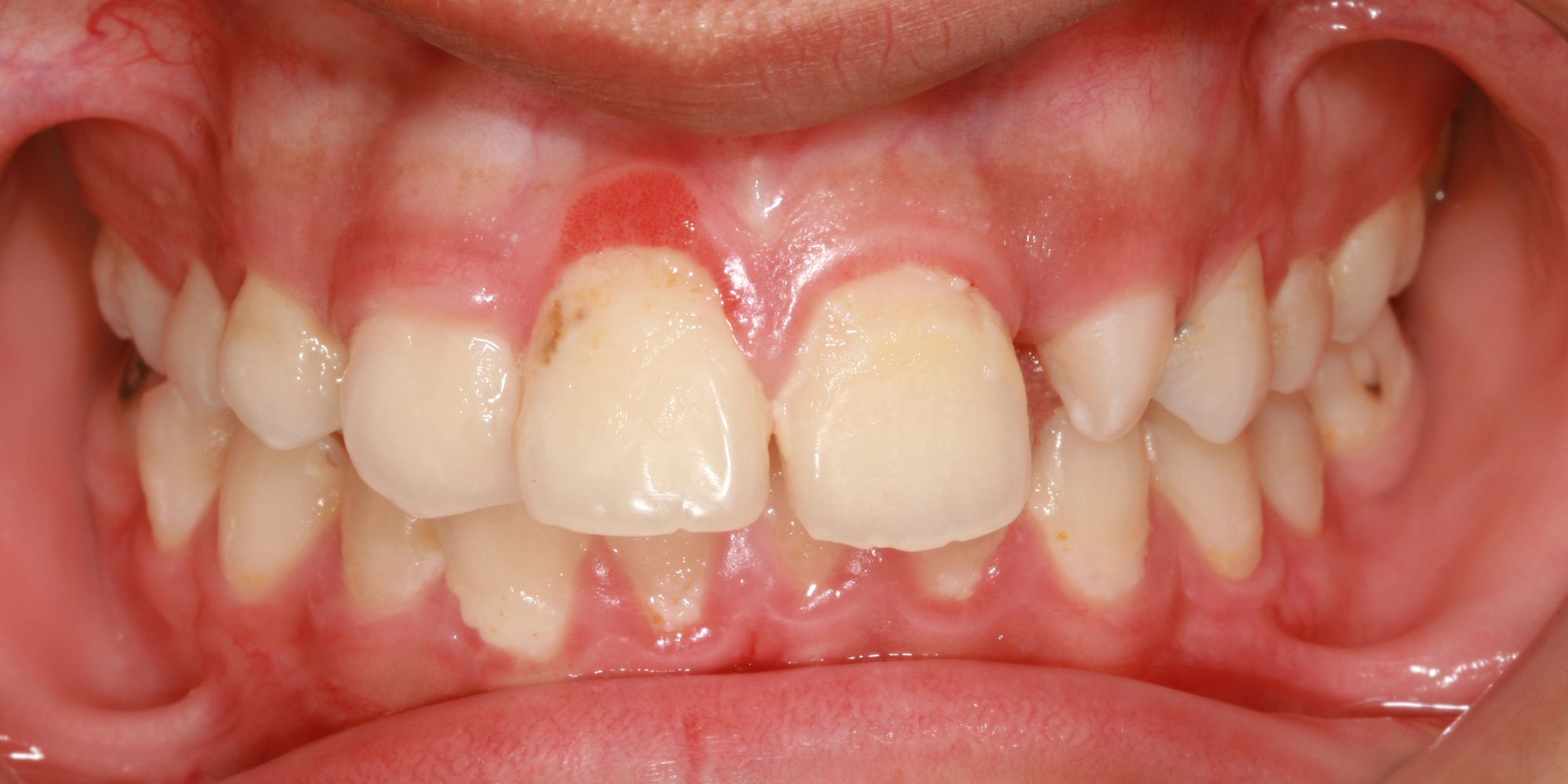
Recognizing the symptoms of gingivitis is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Some of the common symptoms to look out for include red, swollen and sensitive gums, bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, receding gums and pockets between the teeth and gums. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to consult your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
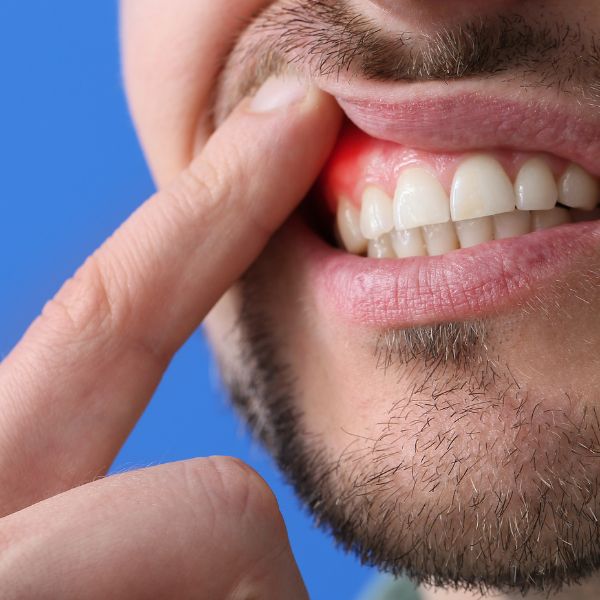

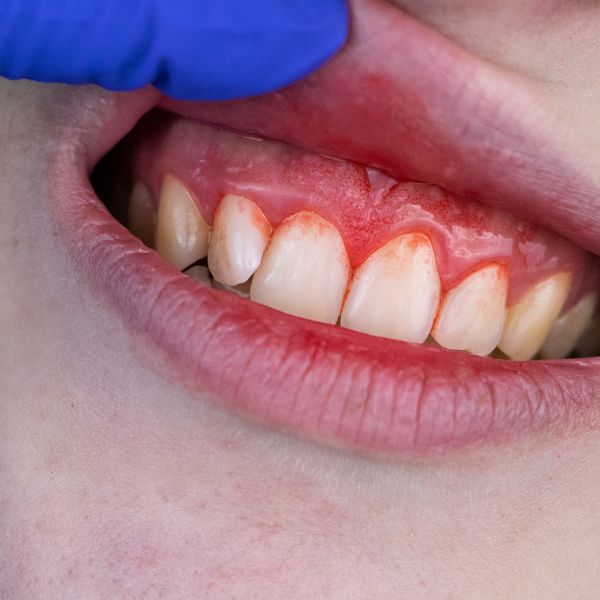
The importance of early detection and treatment
Early detection and treatment of gingivitis is vital to prevent the condition from progressing to a more serious form of gum disease called periodontitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to destruction of gum tissue and the bone that supports the teeth, ultimately resulting in tooth loss. Regular dental checkups and maintaining good oral hygiene practices at home can help detect and treat gingivitis in its early stages, preventing further complications.
Diagnosis of gingivitis
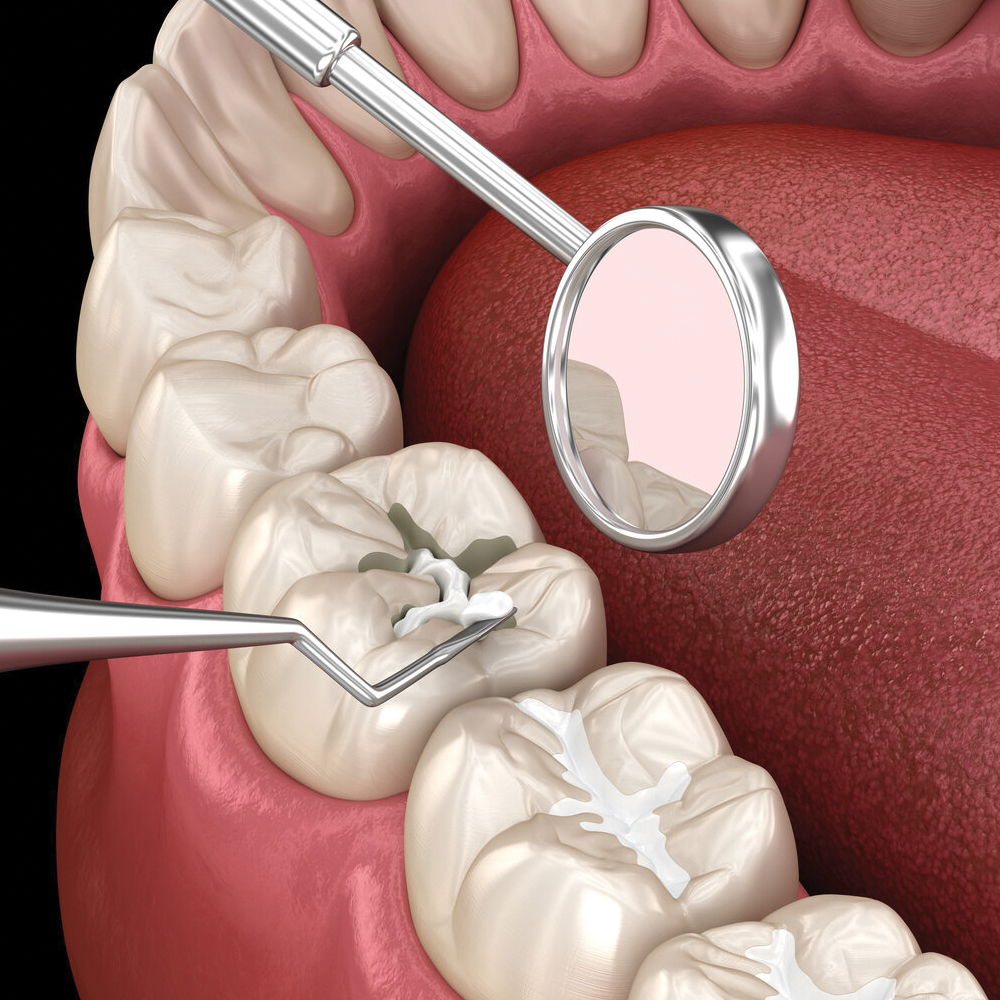
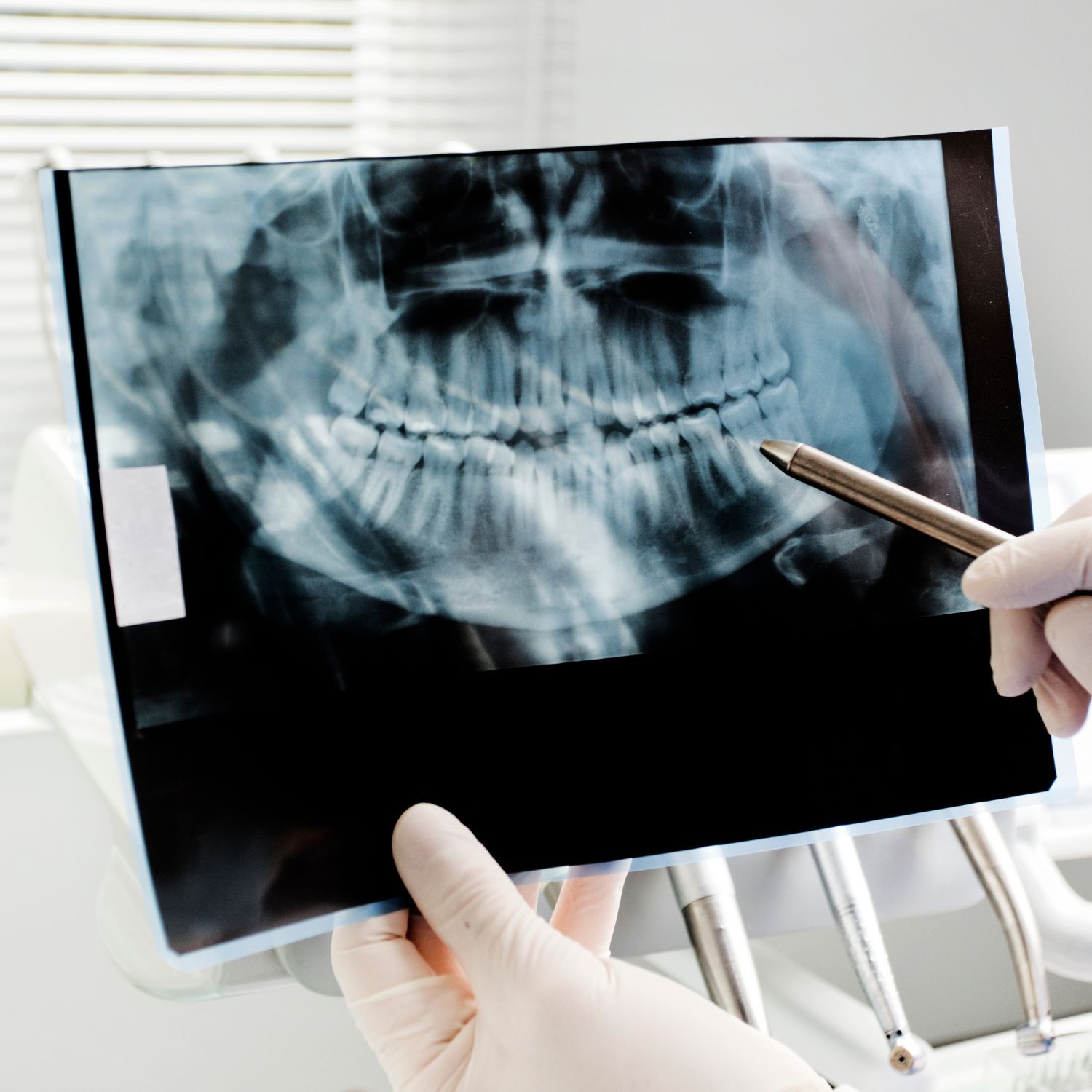
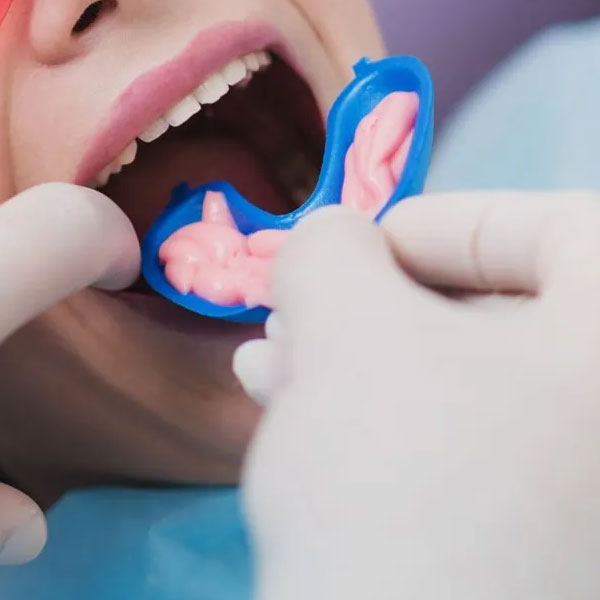
To diagnose gingivitis, the dentist will perform a thorough examination of your mouth and gums. He will check for signs of inflammation, bleeding and measure the depth of any pockets that may have formed between your teeth and gums. The dentist may also take dental x-rays to assess the condition of the bone that supports your teeth. Based on the findings, he will determine the severity of the gingivitis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Preventive measures for the treatment of gingivitis
Prevention is key when it comes to gingivitis. Maintaining good oral hygiene is the most effective way to prevent the development of gingivitis. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in your mouth. In addition, it is important to have a balanced diet, limit sugary foods and drinks and avoid tobacco products, as they can contribute to gum disease.
Request an appointment
Fawq Gingivitis Treatment
Does gingivitis cause pain?
One of the most frequently asked questions about gingivitis is whether it causes pain. The answer to this question is not a simple yes or no. While dental gingivitis itself may not cause significant pain, it can lead to other complications that result in discomfort.
When plaque and bacteria build up along the gum line, the gums become inflamed. This inflammation is the hallmark of gingivitis. While some people may not feel pain, others may notice that their gums become sensitive and swollen. Additionally, the gums may bleed easily, especially when brushing or flossing.
If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease. Periodontitis can cause pain and discomfort as it leads to the destruction of the tissues and bones that support the teeth. Therefore, it is vital to treat gingivitis teeth promptly to prevent further complications.
Is gingivitis contagious?
One of the most prevalent myths surrounding gingivitis is whether or not it is contagious.
Gingivitis is not a contagious disease. It cannot be spread from one person to another through direct contact or airborne particles. The main cause of gingivitis is plaque build-up on the teeth and gums. Plaque is a sticky film that contains bacteria, which can irritate the gums and cause inflammation. Therefore, the development of gingivitis depends mainly on individual oral hygiene practices and not on infectious factors.
Is it easy to get gingivitis in children?
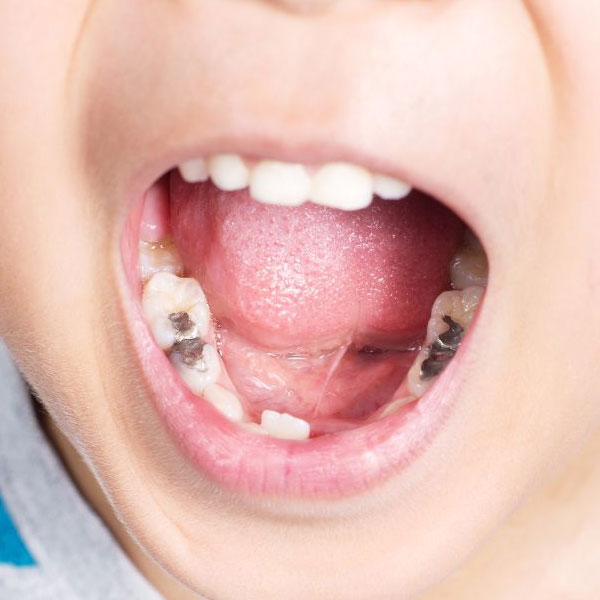
The answer is yes. While gingivitis is more common in adults, it can affect children as well, and it's important for parents to be aware of the signs and symptoms. Diagnosing gingivitis in children can be a bit difficult as the symptoms can be subtle or easily confused with other oral health issues.
When it comes to diagnosing gingivitis in children, parents should pay attention to certain indicators. One of the main signs is red, swollen and sensitive gums. If your child's gums look inflamed or bleed easily when brushing or flossing, it could be a sign of gingivitis. Bad breath is another common symptom, as bacteria in the mouth release foul-smelling gases. Additionally, if you notice a change in your child's bite or complain of pain when eating, it's worth considering gingivitis as a possible cause.
Are there preparations that can help fight gingivitis?
Toothpastes and mouthwashes can help prevent as well as fight gingivitis.
How long does gingivitis treatment last?
The duration of gingivitis treatment can vary depending on several factors. In general, the earlier the condition is diagnosed and treated, the shorter the duration of treatment. Mild cases of gingivitis can often resolve within a few weeks with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care.
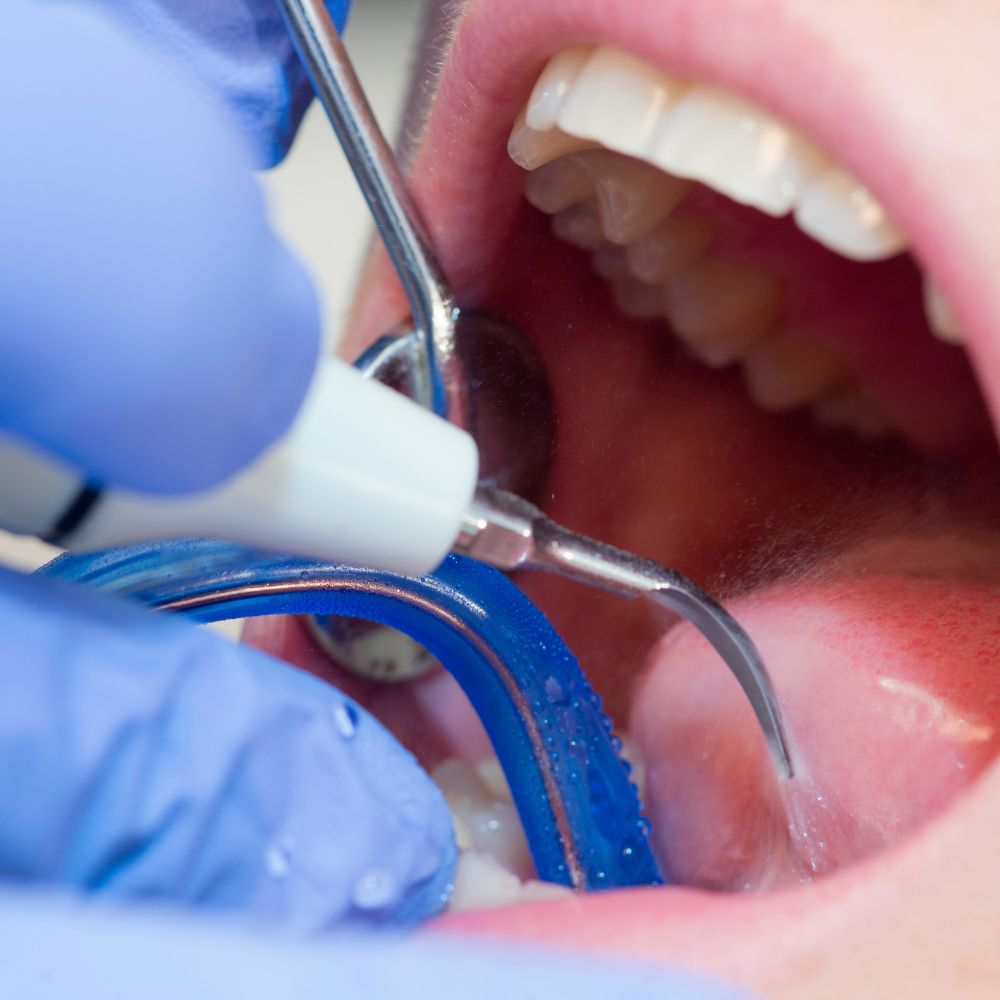
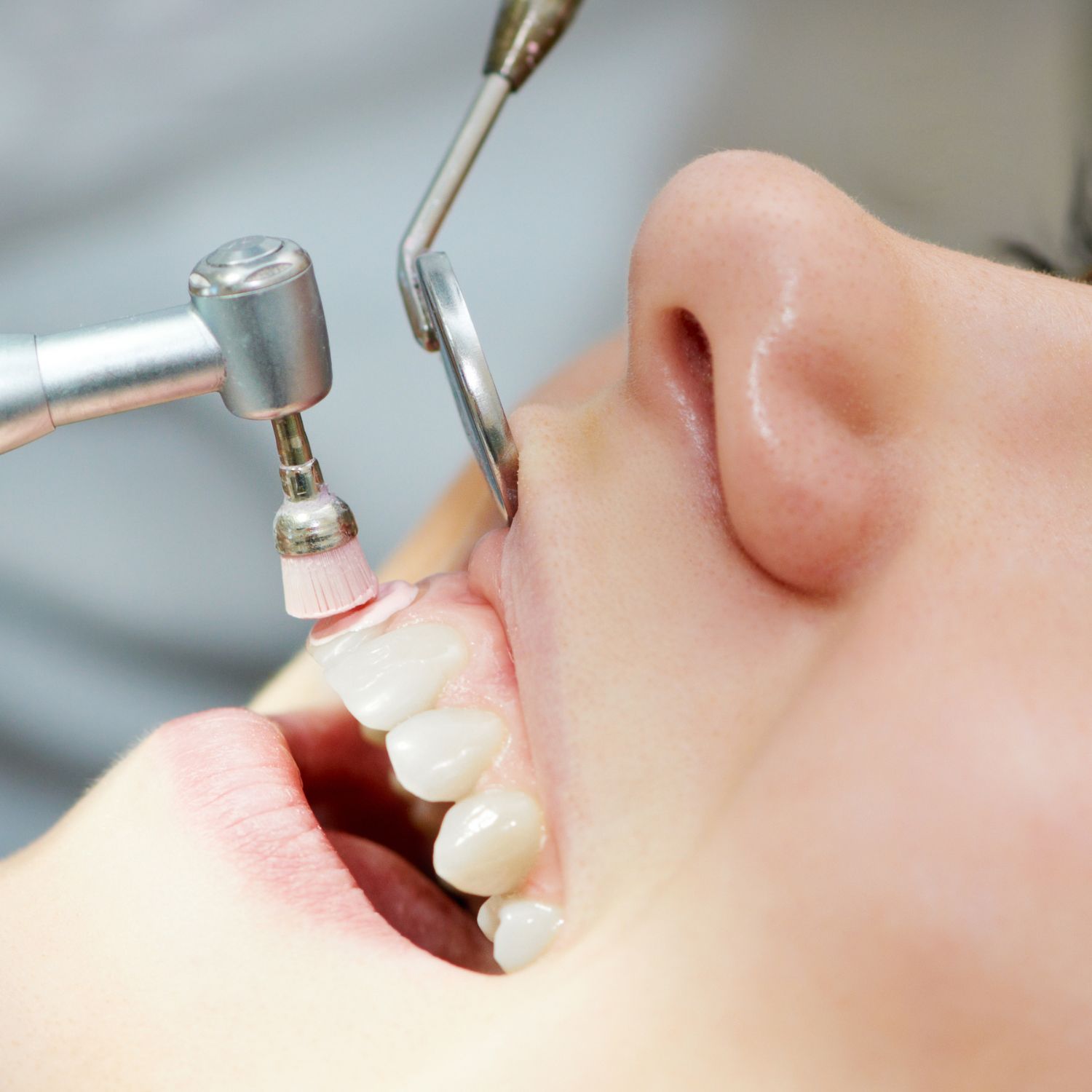
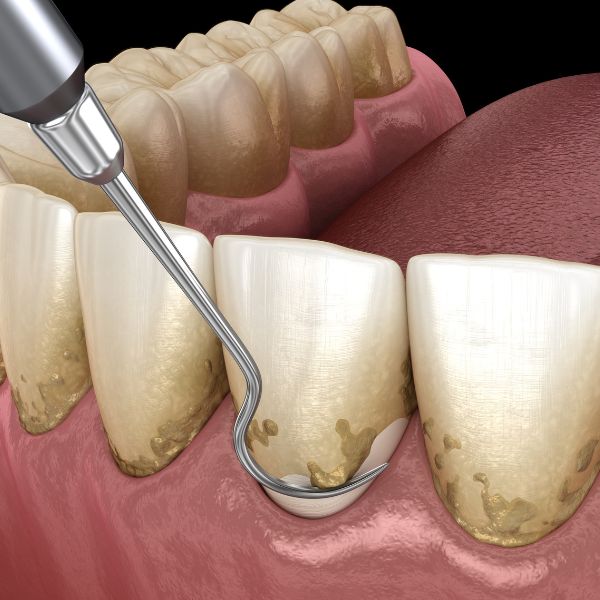
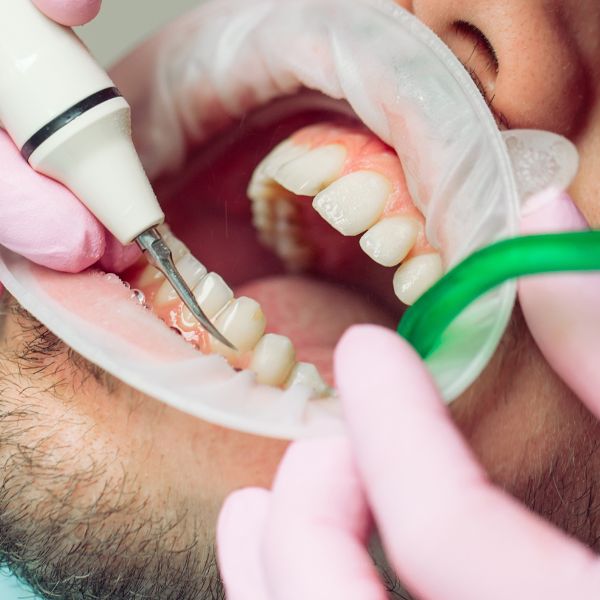
However, if the condition has progressed and become more severe, the duration of treatment may be longer. Advanced stages of gingivitis may require more intensive treatments, such as deep cleaning or scaling and denervation. These procedures involve removing plaque and tartar build-up from the teeth and roots, which may take several visits to complete.